Cannabinol (CBN): A Comprehensive Overview
Cannabinol (CBN) is a cannabinoid derived from the cannabis plant. It is often regarded as a minor cannabinoid, as it typically occurs in lower concentrations compared to THC or CBD. CBN is unique in that it forms as a degradation product of THC—as THC is exposed to oxygen and light, it converts to CBN over time.
Despite its limited presence in cannabis, CBN has garnered significant attention for its potential therapeutic properties, particularly for its sedative effects and potential role in sleep enhancement.
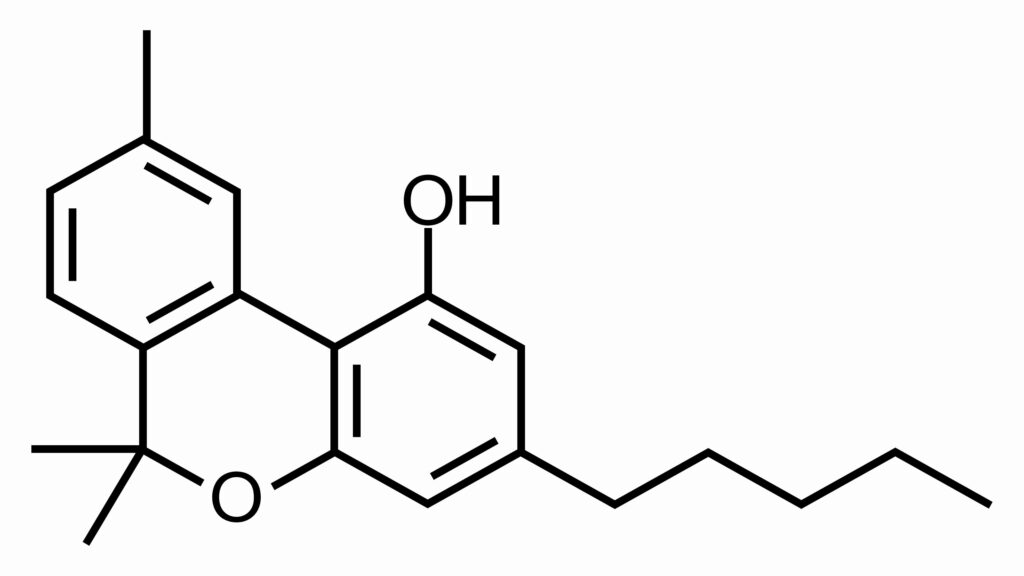
Molecular Structure of CBN
CBN has the molecular formula C₂₁H₂₆O₂, with a structure that is similar to THC, though it lacks the double bond responsible for THC’s psychoactivity. This distinction is critical in understanding the differences in effects between these cannabinoids.
Definition and Background
CBN is recognized for its non-intoxicating properties, meaning it does not produce the “high” typically associated with THC. This makes CBN particularly appealing in medical applications where psychoactive effects are undesirable. Although CBN was among the first cannabinoids to be isolated from cannabis, research on its properties remains relatively sparse compared to its more famous counterparts, THC and CBD.
CBN Significance in the Cannabis Plant
CBN’s formation as a degradation product of THC gives it a unique role in aged cannabis. Cannabis that has been stored for long periods often contains higher levels of CBN, as THC slowly breaks down over time. This characteristic has made CBN particularly popular in certain wellness products, especially sleep aids and relaxation formulas.
Chemical Nature and Biosynthesis
Biosynthetic Pathway
Unlike other cannabinoids, CBN is not produced directly by the cannabis plant. Instead, it forms when tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (THCA), the precursor to THC, oxidizes over time. This process is typically accelerated by heat or exposure to oxygen, which leads to the breakdown of THC into CBN.
Therapeutic Potentials of CBN
Sedative Effects
CBN is often associated with its sedative properties, making it a potential option for individuals seeking to improve sleep quality. This property has made CBN a popular ingredient in sleep-aid products, although more clinical studies are needed to validate its efficacy in humans.
Pain Relief
While CBN is not as potent as CBG for pain relief, it has shown mild analgesic effects in early studies. This makes it a candidate for use in combination with other cannabinoids like CBD, CBG and THC to provide balanced pain management without significant psychoactivity.
Anti-inflammatory Properties
CBN also exhibits anti-inflammatory potential, which could make it useful in treating conditions characterized by chronic inflammation, such as arthritis and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
Antibacterial Effects
Recent research suggests that CBN has antibacterial properties, particularly against strains of bacteria that are resistant to antibiotics, such as MRSA. This opens the door for potential use in developing new antibiotic treatments.
Neuroprotective Properties
Preliminary studies indicate that CBN may have neuroprotective effects, particularly in the context of ALS and Parkinson’s disease. While more research is required, these findings suggest CBN could play a role in protecting against neurodegenerative disorders.
Appetite Stimulation
Unlike CBD, which is often associated with appetite suppression, CBN may act as a mild appetite stimulant. This makes it a potential candidate for patients suffering from appetite loss due to chronic illnesses like cancer or HIV/AIDS.
Non-Psychotropic Properties
CBN is non-psychoactive, meaning it does not induce the “high” associated with THC. This characteristic, combined with its potential therapeutic benefits, makes CBN an attractive option for patients seeking relief without the cognitive impairment often caused by THC.
Potential Medical Applications of CBN
- Sleep Aid: CBN is commonly marketed for its sedative properties and is often included in formulations aimed at improving sleep.
- Chronic Pain: Early studies suggest CBN may help with chronic pain management, particularly when used in conjunction with other cannabinoids.
- Inflammatory Conditions: CBN’s anti-inflammatory effects may benefit individuals with chronic inflammatory conditions like arthritis or IBD.
- Neurodegenerative Diseases: Preliminary research into CBN’s neuroprotective properties points to its potential in treating diseases like ALS and Parkinson’s.
- Antibacterial Agent: CBN has shown promise in combating drug-resistant bacterial infections, including MRSA.
Interaction with the Endocannabinoid System
CBN interacts with the body’s endocannabinoid system (ECS), specifically the CB1 and CB2 receptors. Its affinity for these receptors is relatively weak compared to THC, which may explain why CBN does not produce a strong psychoactive effect. However, its ability to influence the CB2 receptors suggests that it could play a role in regulating immune responses and reducing inflammation.
References
- Borrelli, F., et al. (2013). “Beneficial Effect of Cannabinol on Inflammatory Bowel Disease.” Biochemical Pharmacology. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2013.01.017
- Granja, A. G., et al. (2012). “A Walk Through Cannabinoid Potentials in Cancer Therapy.” BioMed Research International. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/195782
- Morales, P., et al. (2017). “Molecular Targets of the Phytocannabinoids: A Complex Picture.” Progress in the Chemistry of Organic Natural Products. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-45541-9_4
- Turner, S. E., et al. (2017). “Molecular Pharmacology of Phytocannabinoids.” Phytocannabinoids: Unraveling the Complex Chemistry and Pharmacology of Cannabis sativa. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-45541-9_3
- Anderson, L. L., et al. (2021). “Antibacterial and Neuroprotective Effects of Cannabinol in Preclinical Models.” ACS Chemical Neuroscience. https://doi.org/10.1021/acschemneuro.0c00677
In Summary
While much remains to be discovered about CBN, early research suggests that this cannabinoid has significant potential in areas such as sleep, pain management, and inflammation control. As research continues, CBN may become a critical component of future cannabis-based therapies.

