Intro to CBD (Cannabidiol)
CBD, or cannabidiol, is a compound extracted from the cannabis plant. Like CBG, it is non-psychoactive, meaning it doesn’t induce the “high” that THC does. CBD has gained widespread attention due to its possible health benefits, including alleviating anxiety, reducing chronic pain, and decreasing inflammation.

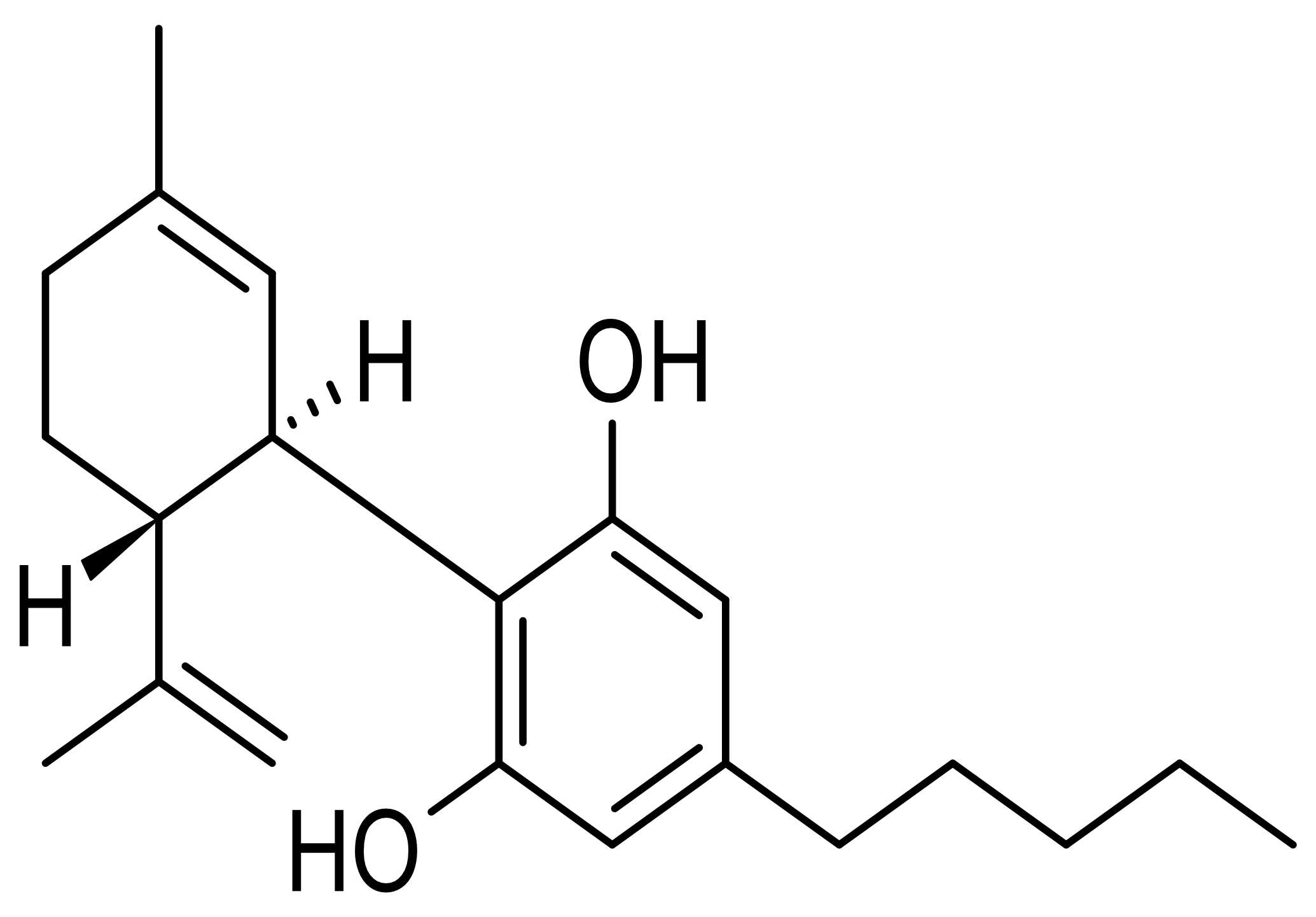
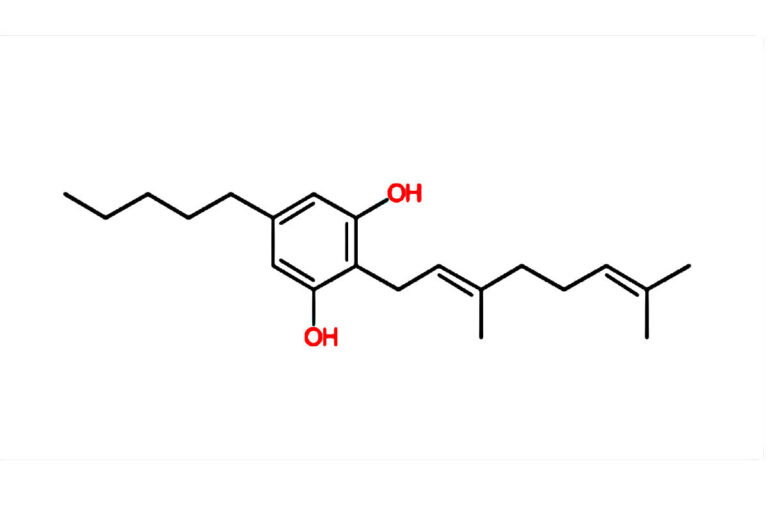
Molecular Structure of CBD
Cannabidiol (CBD) has the molecular formula C₂₁H₃₀O₂, consisting of 21 carbon atoms, 30 hydrogen atoms, and 2 oxygen atoms. Its structure is distinct from tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and other cannabinoids, which is critical to its interaction with the human body.
Unlike THC, which binds directly to the brain’s CB1 receptors and triggers psychoactive effects, CBD does not have a strong affinity for these receptors. Instead, it influences the endocannabinoid system (ECS) through indirect pathways. This unique interaction is what allows CBD to provide therapeutic benefits without producing a “high.”
Definition and Background
CBD is just one of the more than 100 cannabinoids found in the cannabis plant. It is most commonly sourced from hemp, a variety of cannabis that contains less than 0.3% THC, which allows it to be legally accepted in numerous regions. CBD is available in several forms, such as oils, tinctures, and topicals, each serving various health and wellness purposes.
Significance in the Cannabis Plant
The significance of CBD lies in its therapeutic potential without causing intoxication. Unlike THC, which can alter cognition, CBD interacts with the endocannabinoid system (ECS) in a more subtle way, promoting homeostasis and offering relief for conditions such as anxiety, epilepsy, and inflammation. Additionally, CBD does not have a strong binding affinity for CB1 or CB2 receptors, but it influences these and other receptors, such as serotonin and TRPV1, making it a versatile therapeutic option.
Full-Spectrum vs. Broad-Spectrum CBD
Full-Spectrum CBD
Full-spectrum CBD contains all the naturally occurring cannabinoids, terpenes, and flavonoids found in the cannabis plant, including trace amounts of THC (less than 0.3%). This combination creates the “entourage effect,” where the presence of multiple cannabinoids enhances the therapeutic effects of each compound
Key Benefits:
Enhanced efficacy due to the entourage effect.
Potentially more effective for chronic pain, anxiety, and inflammation.
Limitations:
May result in a positive drug test due to trace THC.
Not suitable for individuals sensitive to THC.
Broad-Spectrum CBD
Broad-spectrum CBD also contains a range of cannabinoids and terpenes, but without any THC. This makes it ideal for individuals seeking the benefits of the entourage effect without the risk of consuming THC.
Key Benefits:
Provides the entourage effect without THC.
Suitable for individuals in zero-THC professions or regions with strict THC regulations.
Limitations:
May be less potent than full-spectrum CBD due to the absence of THC.
Delta-9 THC and Delta-8 THC
Delta-9 THC
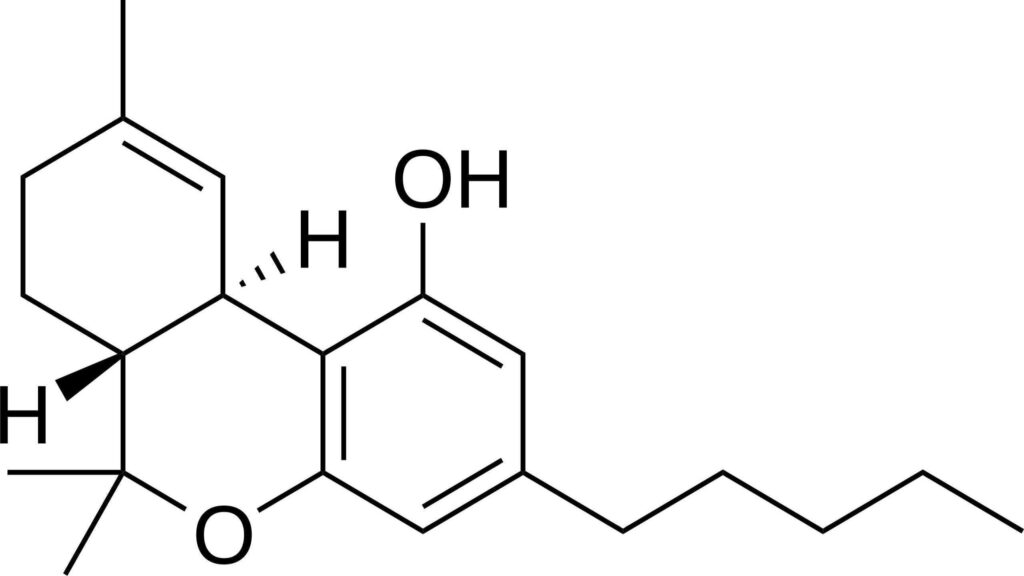
Delta-9 THC is the most well-known psychoactive cannabinoid in cannabis. It binds strongly to CB1 receptors in the brain, leading to the characteristic “high” and influencing mood, appetite, and perception. While effective for pain and nausea, its psychoactive nature can impair cognitive functions.
Key Benefits:
Effective for pain relief, nausea, and appetite stimulation.
Commonly used in both recreational and medical cannabis products.
imitations:
Causes psychoactive effects.
Potential for dependency and side effects like anxiety or paranoia.
Delta-8 THC
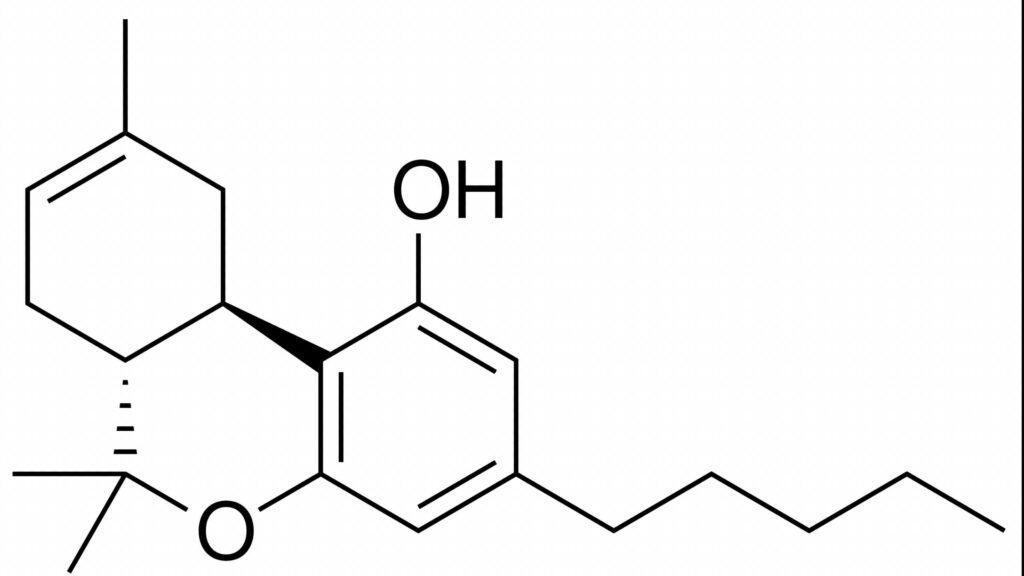
Delta-8 THC is a minor cannabinoid, similar in structure to Delta-9 THC but with milder psychoactive effects. It binds to the CB1 receptor but with lower affinity, resulting in a less intense “high.” Delta-8 is gaining popularity for its reduced psychoactivity and potential benefits in pain relief and anxiety.
Key Benefits:
Milder psychoactive effects compared to Delta-9 THC.
Potential therapeutic benefits for pain, nausea, and anxiety.
Limitations:
Psychoactive, though less so than Delta-9 THC.
Still subject to varying legal restrictions.
THCA (Tetrahydrocannabinolic Acid)
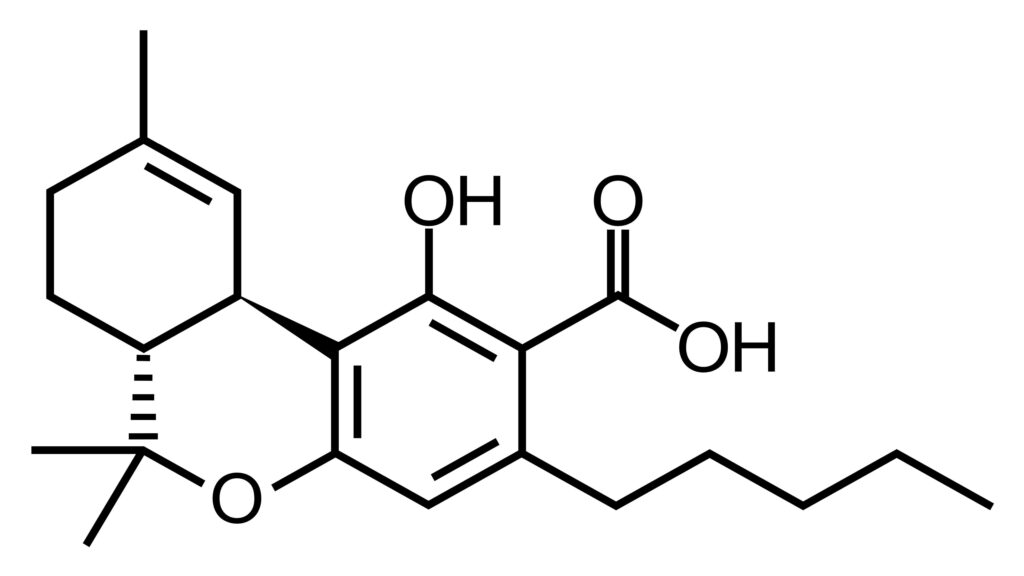
THCA is the non-psychoactive precursor to THC. Found in raw cannabis, it converts to THC through decarboxylation, typically triggered by heat (smoking, vaping, or cooking). THCA itself offers potential health benefits, including anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective effects, without causing a high.
Key Benefits:
Anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective properties.
Non-psychoactive, making it appealing for those seeking health benefits without intoxication.
Limitations:
Converts to THC when heated, which may lead to psychoactive effects if not used correctly.
Therapeutic Applications
CBD and related cannabinoids are being explored for various therapeutic applications, offering potential benefits in several areas of health.
Anxiety and Depression: Studies show that CBD interacts with serotonin receptors, particularly the 5-HT1A receptor, which plays a role in mood regulation. This interaction may help stabilize mood and alleviate anxiety without the side effects often seen with conventional antidepressants (Blessing, E. M., Steenkamp, M. M., Manzanares, J., & Marmar, C. R., 2015).
Chronic Pain: CBD’s ability to modulate pain pathways and reduce inflammation has been documented in research. It influences the body’s response to pain, offering relief for conditions such as arthritis and multiple sclerosis (Russo, E. B., 2008).
Epilepsy: The FDA-approved drug Epidiolex, which is derived from CBD, has been shown to effectively treat certain forms of epilepsy, including Dravet syndrome and Lennox-Gastaut syndrome. This illustrates CBD’s effectiveness in controlling seizures (Devinsky, O., Patel, A. D., Thiele, E. A., et al., 2018).
Neuroprotection: Both CBD and THCA exhibit neuroprotective properties. Research suggests they may help protect neurons, offering potential therapeutic use in treating neurodegenerative conditions such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases (Iuvone, T., Esposito, G., De Filippis, D., Scuderi, C., & Steardo, L., 2009).
Inflammatory Conditions: CBD is well-recognized for its anti-inflammatory properties. It has shown promise in treating inflammatory conditions like inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and rheumatoid arthritis by targeting the inflammatory response at a molecular level (Borrelli, F., Fasolino, I., Romano, B., et al., 2013).
References
Blessing, E. M., Steenkamp, M. M., Manzanares, J., & Marmar, C. R. (2015). Cannabidiol as a potential treatment for anxiety disorders. Neurotherapeutics, 12(4), 825-836. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13311-015-0387-1
Russo, E. B. (2008). Cannabinoids in the management of difficult to treat pain. Therapeutics and Clinical Risk Management, 4(1), 245-259. https://doi.org/10.2147/tcrm.s1929
Devinsky, O., Patel, A. D., Thiele, E. A., et al. (2018). Randomized, dose-ranging safety trial of cannabidiol in Dravet syndrome. New England Journal of Medicine, 378(20), 1888-1897. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1714631
Iuvone, T., Esposito, G., De Filippis, D., Scuderi, C., & Steardo, L. (2009). Cannabidiol: A promising drug for neurodegenerative disorders? CNS Neuroscience & Therapeutics, 15(1), 65-75. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1755-5949.2008.00065.x
Borrelli, F., Fasolino, I., Romano, B., et al. (2013). Beneficial effect of the non-psychotropic plant cannabinoid cannabigerol on experimental inflammatory bowel disease. Biochemical Pharmacology, 85(9), 1306-1316. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2013.01.017
In Summary
CBD, along with related cannabinoids like Delta-9 THC, Delta-8 THC, and THCA, represents a growing field of interest for its broad range of therapeutic applications. Understanding the distinctions between full-spectrum, broad-spectrum, and isolate products helps consumers make informed decisions based on their health goals and concerns about THC content. The non-psychoactive nature of CBD and its potential health benefits continue to drive its popularity as a natural remedy for various conditions.